Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
伊藤 孝; 門野 良典*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(4), p.044602_1 - 044602_7, 2024/04
We propose a model to describe the fluctuations in the internal magnetic field due to ion dynamics observed in muon spin relaxation ( SR) by an Edwards-Anderson-type autocorrelation function that separates the quasi-static and dynamic components of the correlation by the parameter
SR) by an Edwards-Anderson-type autocorrelation function that separates the quasi-static and dynamic components of the correlation by the parameter  (where
(where 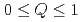 ). Our Monte Carlo simulations for this model showed that the time evolution of muon spin polarization deviates significantly from the Kubo-Toyabe function. To further validate the model, the results of simulations were compared with the
). Our Monte Carlo simulations for this model showed that the time evolution of muon spin polarization deviates significantly from the Kubo-Toyabe function. To further validate the model, the results of simulations were compared with the  SR spectra observed in a hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite FAPbI
SR spectra observed in a hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite FAPbI [with FA referring to HC(NH
[with FA referring to HC(NH )
) ], where local field fluctuations associated with the rotational motion of FA molecules and quasi-static fields from the PbI
], where local field fluctuations associated with the rotational motion of FA molecules and quasi-static fields from the PbI lattice are presumed to coexist. The least-squares curve fitting showed reasonable agreement with the model with
lattice are presumed to coexist. The least-squares curve fitting showed reasonable agreement with the model with 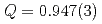 , and the fluctuation frequency of the dynamical component was obtained. This result opens the door to the possibility of experimentally distinguishing fluctuations due to the dynamics of ions around muons from those due to the self-diffusion of muons. On the other hand, it suggests the need to carefully consider the spin relaxation function when applying
, and the fluctuation frequency of the dynamical component was obtained. This result opens the door to the possibility of experimentally distinguishing fluctuations due to the dynamics of ions around muons from those due to the self-diffusion of muons. On the other hand, it suggests the need to carefully consider the spin relaxation function when applying  SR to the issue of ion dynamics.
SR to the issue of ion dynamics.
 CoSi
CoSi山内 宏樹; Sari, D. P.*; 安井 幸夫*; 坂倉 輝俊*; 木村 宏之*; 中尾 朗子*; 大原 高志; 本田 孝志*; 樹神 克明; 井川 直樹; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013144_1 - 013144_9, 2024/02
 -Mn-type family alloys Mn
-Mn-type family alloys Mn
 have three-dimensional antiferromagnetic (AFM) corner-shared triangular network. The antiferromagnet Mn
have three-dimensional antiferromagnetic (AFM) corner-shared triangular network. The antiferromagnet Mn RhSi shows magnetic short-range order (SRO) over a wide temperature range of approximately 500 K above the N
RhSi shows magnetic short-range order (SRO) over a wide temperature range of approximately 500 K above the N el temperature
el temperature  = 190 K. Mn
= 190 K. Mn CoSi has the smallest lattice parameter and the lowest
CoSi has the smallest lattice parameter and the lowest  in the family compounds. The quantum critical point (QCP) from AFM to the quantum paramagnetic state is expected near a cubic lattice parameter of 6.15
in the family compounds. The quantum critical point (QCP) from AFM to the quantum paramagnetic state is expected near a cubic lattice parameter of 6.15  of Mn
of Mn CoSi is only 140 K, quantum critical behavior is observed in Mn
CoSi is only 140 K, quantum critical behavior is observed in Mn CoSi as the enhancement of the electronic specific heat coefficient
CoSi as the enhancement of the electronic specific heat coefficient  . We study how the magnetic SRO appears in Mn
. We study how the magnetic SRO appears in Mn CoSi by using neutron scattering,
CoSi by using neutron scattering,  SR, and physical property measurements. The experimental results show that the neutron scattering intensity of the magnetic SRO does not change much regardless of the suppressed magnetic moment in the long-range magnetic ordered state compared to those of Mn
SR, and physical property measurements. The experimental results show that the neutron scattering intensity of the magnetic SRO does not change much regardless of the suppressed magnetic moment in the long-range magnetic ordered state compared to those of Mn RhSi. The initial asymmetry drop ratio of
RhSi. The initial asymmetry drop ratio of  SR above
SR above  becomes small, and the magnetic SRO temperature
becomes small, and the magnetic SRO temperature 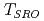 is suppressed to 240 K. The results suggest that the Mn
is suppressed to 240 K. The results suggest that the Mn CoSi is close to the QCP in the Mn
CoSi is close to the QCP in the Mn
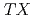 system.
system.
伊藤 孝; 髭本 亘; 下村 浩一郎*
Physical Review B, 108(22), p.224301_1 - 224301_11, 2023/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In positive muon spin rotation and relaxation ( SR) spectroscopy, positive muons (
SR) spectroscopy, positive muons ( ) implanted into solid oxides are conventionally treated as immobile spin-probes at interstitial sites below room temperature. This is because each
) implanted into solid oxides are conventionally treated as immobile spin-probes at interstitial sites below room temperature. This is because each  is thought to be tightly bound to an oxygen atom in the host lattice to form a muonic analogue of the hydroxy group. On the basis of this concept, anomalies in
is thought to be tightly bound to an oxygen atom in the host lattice to form a muonic analogue of the hydroxy group. On the basis of this concept, anomalies in  SR spectra observed in oxides have been attributed in most cases to the intrinsic properties of host materials. On the other hand, global
SR spectra observed in oxides have been attributed in most cases to the intrinsic properties of host materials. On the other hand, global  diffusion with an activation energy of
diffusion with an activation energy of  0.1~eV has been reported in some chemically-substituted perovskite oxides at cryogenic temperatures, although the reason for the small activation energy despite the formation of the strong O
0.1~eV has been reported in some chemically-substituted perovskite oxides at cryogenic temperatures, although the reason for the small activation energy despite the formation of the strong O bond has not yet been quantitatively understood. In this study, we investigated interstitial
bond has not yet been quantitatively understood. In this study, we investigated interstitial  diffusion in the perovskite oxide lattice using KTaO
diffusion in the perovskite oxide lattice using KTaO cubic perovskite as a model system. We used the
cubic perovskite as a model system. We used the  SR method and density functional theory calculations along with the harmonic transition state theory to study this phenomenon both experimentally and theoretically. Experimental activation energies for global
SR method and density functional theory calculations along with the harmonic transition state theory to study this phenomenon both experimentally and theoretically. Experimental activation energies for global  diffusion obtained below room temperature were less than a quarter of the calculated classical potential barrier height for a bottleneck
diffusion obtained below room temperature were less than a quarter of the calculated classical potential barrier height for a bottleneck  transfer path. The reduction in the effective barrier height could be explained by the harmonic transition state theory with a zero-point energy correction; a significant difference in zero-point energies for
transfer path. The reduction in the effective barrier height could be explained by the harmonic transition state theory with a zero-point energy correction; a significant difference in zero-point energies for  at the positions in the O
at the positions in the O bonding equilibrium state and a bond-breaking transition state was the primary cause of the reduction. This suggests that the assumption of immobile
bonding equilibrium state and a bond-breaking transition state was the primary cause of the reduction. This suggests that the assumption of immobile  in solid oxides is not always satisfied since such a significant decrease in diffusion barrier height can also occur in other oxides.
in solid oxides is not always satisfied since such a significant decrease in diffusion barrier height can also occur in other oxides.
 SR) methods
SR) methods伊藤 孝; 下村 浩一郎*
Hydrogenomics; The Science of Fully Utilizing Hydrogen (Internet), p.43 - 49, 2023/03
A brief introduction to the muon spin rotation, relaxation, and resonance ( SR) methods is given for researchers and students involved in hydrogen science research. The text includes several examples of how the
SR) methods is given for researchers and students involved in hydrogen science research. The text includes several examples of how the  SR methods can be used to elucidate the behavior of hydrogen in materials.
SR methods can be used to elucidate the behavior of hydrogen in materials.
 =
=  quasikagome-lattice compound CeRh
quasikagome-lattice compound CeRh Pd
Pd Sn investigated using muon spin relaxation and neutron scattering
Sn investigated using muon spin relaxation and neutron scatteringTripathi, R.*; Adroja, D. T.*; Ritter, C.*; Sharma, S.*; Yang, C.*; Hillier, A. D.*; Koza, M. M.*; Demmel, F.*; Sundaresan, A.*; Langridge, S.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 106(6), p.064436_1 - 064436_17, 2022/08
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:34.67(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present the results of muon spin relaxation ( SR) and neutron scattering measurements on the Ce-based quasikagome lattice CeRh
SR) and neutron scattering measurements on the Ce-based quasikagome lattice CeRh Pd
Pd Sn (
Sn ( = 0.1 to 0.75). Our
= 0.1 to 0.75). Our  SR results reveal the absence of both static long-range magnetic order and spin freezing down to 0.05 K in the
SR results reveal the absence of both static long-range magnetic order and spin freezing down to 0.05 K in the  = 0.1 sample, which is consistent with neutron scattering results. The weak temperature-dependent plateaus of the dynamic spin fluctuations below 0.2 K in zero field together with its longitudinal-field (LF) dependence indicate the presence of dynamic spin fluctuations persisting even at 0.05 K without static magnetic order. We argue that such a behavior for
= 0.1 sample, which is consistent with neutron scattering results. The weak temperature-dependent plateaus of the dynamic spin fluctuations below 0.2 K in zero field together with its longitudinal-field (LF) dependence indicate the presence of dynamic spin fluctuations persisting even at 0.05 K without static magnetic order. We argue that such a behavior for  = 0.1 can be attributed to a metallic spin-liquid-like ground state near the quantum critical point in the frustrated Kondo lattice. The LF-
= 0.1 can be attributed to a metallic spin-liquid-like ground state near the quantum critical point in the frustrated Kondo lattice. The LF- SR study suggests that the out of kagome plane spin fluctuations are responsible for the spin-liquid behavior.
SR study suggests that the out of kagome plane spin fluctuations are responsible for the spin-liquid behavior.
 SR as a potential tool for depth-resolved detection of oxygen vacancies in perovskite oxides
SR as a potential tool for depth-resolved detection of oxygen vacancies in perovskite oxides伊藤 孝; 髭本 亘; 幸田 章宏*; 下村 浩一郎*
no journal, ,
Oxygen vacancy (V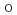 ) is a major defect species in perovskite oxides, having a strong impact on their electrical, optical, and dielectric properties. In spite of its importance, experimental techniques that can directly detect V
) is a major defect species in perovskite oxides, having a strong impact on their electrical, optical, and dielectric properties. In spite of its importance, experimental techniques that can directly detect V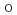 are still limited. Through a series of
are still limited. Through a series of  SR measurements on oxygen-deficient SrTiO
SR measurements on oxygen-deficient SrTiO , we revealed that there is a clear positive correlation between the muon spin relaxation rate and the carrier concentration, which is expected to be roughly proportional to the V
, we revealed that there is a clear positive correlation between the muon spin relaxation rate and the carrier concentration, which is expected to be roughly proportional to the V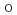 donor concentration. This, together with the variability of muon implantation depth, suggests that
donor concentration. This, together with the variability of muon implantation depth, suggests that  SR spectroscopy is potentially suitable for depth-resolved analysis of V
SR spectroscopy is potentially suitable for depth-resolved analysis of V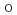 distribution in perovskite oxides, which is complementary to cation vacancy-sensitive techniques, such as positron annihilation spectroscopy.
distribution in perovskite oxides, which is complementary to cation vacancy-sensitive techniques, such as positron annihilation spectroscopy.